When you hit a light switch, plug in your phone, or open your fridge, you’re relying on a massive system that most of us rarely think about. Electricity is something we use constantly, but few of us stop to consider where it actually comes from and how it travels all the way to our homes.
It’s easy to take for granted. After all, it’s always there, powering your morning coffee, your evening TV time, and everything in between. But the journey electricity takes to reach your outlet is long, carefully managed, and full of science, engineering, and planning.
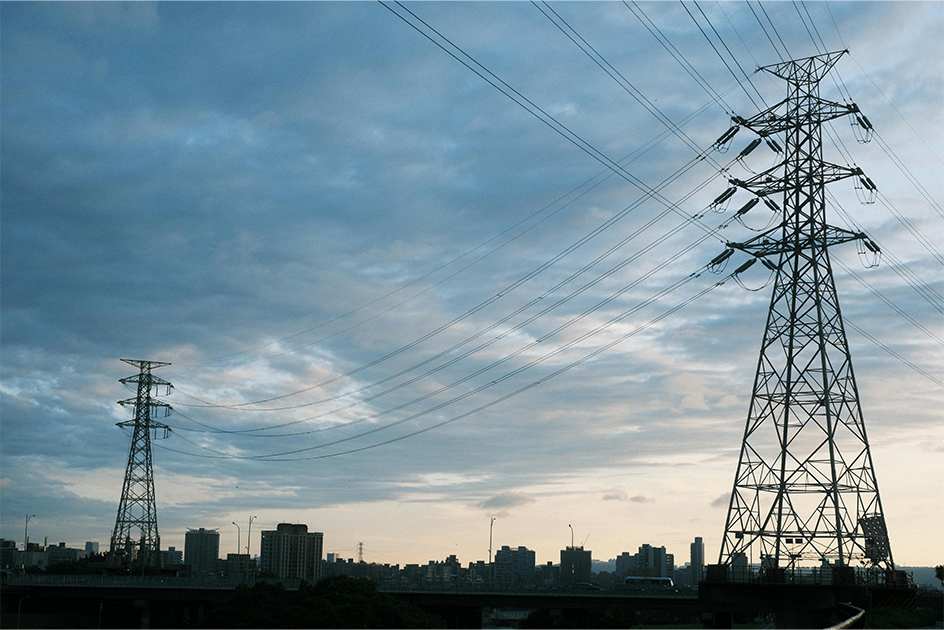

Think of the electricity system like a giant web. It stretches across the entire country, connecting power stations to towns, cities, farms, offices, and homes, and this vast network is often referred to as the grid. Its job is to make sure that electricity is always available where it’s needed and that supply and demand are balanced at all times.
When we talk about “the grid,” we are really talking about a series of connected systems. There’s generation, where the power is created, and then there’s transmission, where it’s moved over long distances. The final part is distribution, where it’s delivered to homes and buildings and all of these parts need to work in sync, every second of every day. Now let’s break it down.
1. Power Generation: Where it all starts
Electricity doesn’t just appear out of nowhere, it starts its life at a power plant. These plants can run on a number of different fuel sources, some cleaner than others.
Many power plants still rely on traditional sources like coal, natural gas, or oil, and these fuels are burned to produce heat, which turns water into steam. That steam then spins huge turbines, which drive generators that create electricity. While this method has powered much of the world for decades, it’s also responsible for a large chunk of our carbon emissions and environmental impact.
In contrast, nuclear power works by splitting atoms of uranium in a process called fission, this releases heat, which is used the same way, to turn water into steam and drive turbines. Nuclear plants produce very low carbon emissions, but they come with their own set of challenges, including how to safely store radioactive waste.
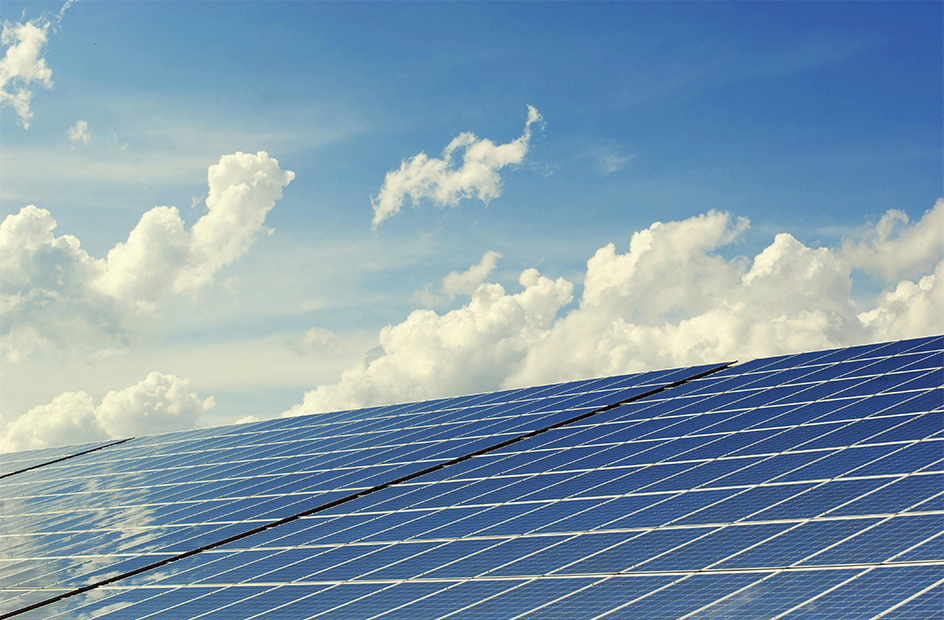

Then there are the renewables. Wind turbines harness the breeze to turn blades, and solar panels capture sunlight and turn it directly into electricity. Hydropower uses flowing water from dams or rivers to spin turbines, and there’s also energy from biomass, tides, and even underground geothermal heat. These sources are cleaner and more sustainable, and they’re becoming more common as the world tries to cut back on pollution.
Regardless of how it’s produced, once electricity is created, it needs to be sent to the people who need it, and that is where transmission comes in.
2. Power Transmission: Moving Electricity Long Distances
Electricity does not travel like a car on a road, but the system works in a similar way. After power is generated at a plant, it needs to be moved, often across hundreds of miles, and to do this efficiently, the electricity is sent at very high voltages. The higher the voltage, the less energy is lost along the way.
You have probably seen those big metal towers with thick wires stretched between them, standing tall across fields or running alongside highways, those are transmission lines. Transmission lines are built to handle high-voltage electricity and move it from power plants to cities and towns.
At certain points, electricity passes through something called a substation. These are important checkpoints that help manage the flow of electricity, switch connections, and change the voltage level. Substations are like intersections where the direction and intensity of traffic are controlled.
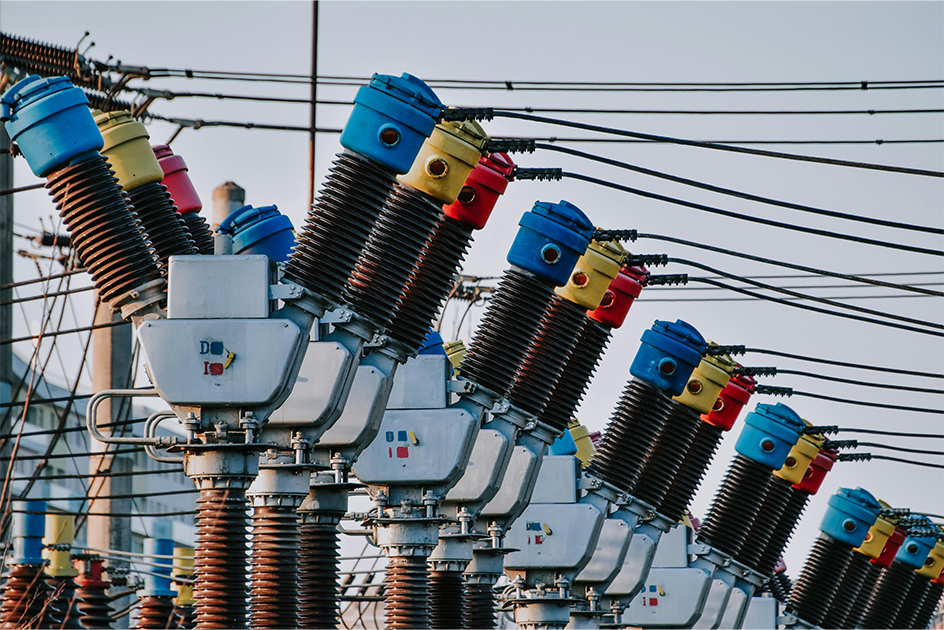

3. Local Distribution: The Final Stretch
After electricity has traveled across the grid, it still needs to reach individual homes. But before that happens, the high voltage has to be lowered to a safer level. That happens at another kind of substation, usually located closer to neighborhoods.
From there, the electricity is carried through smaller wires, often the ones you see on wooden poles or buried underground. These are part of the local distribution system. Along the way, more transformers step the voltage down again to make it safe for use in homes and small businesses.
By the time electricity reaches your house, it’s usually at a voltage of either 120 or 240 volts, depending on the country you live in. From there, it flows through your home’s wiring and into the outlets and appliances you use every day.
4. AC vs. DC: Two AC VS. DC: Two Types of Current
There are two main types of electricity: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Most of what we use in our homes is AC, which means the electrical flow changes direction many times a second. AC is ideal for sending electricity over long distances and works well with transformers that adjust voltage up and down.
DC, on the other hand, flows in only one direction. It is the kind of electricity you get from batteries and solar panels. While DC is not typically used in household wiring, it plays a role in certain technologies and in long-distance transmission in some parts of the world.
5. The Human Side of the Grid
All of this, the generating stations, the transmission lines, the substations, and the local networks, requires a huge amount of coordination. Engineers, technicians, grid operators, and utility workers all play a part in keeping the system running smoothly. Maintenance crews repair damage from storms, and operators monitor demand in real time, on the other hand, energy planners look ahead to make sure future needs will be met.

There is another layer to consider, as more people switch to electric cars, heat pumps, and other electric technologies, demand for electricity is growing. At the same time, we are trying to move away from fossil fuels and invest in clean energy. That means the grid is under pressure to change, and fast.
Knowing how electricity gets to your home might not change how you use it day to day, but it does help you understand what goes on behind the scenes. Every flick of a light switch depends on a vast system of technology, infrastructure, and people working together to deliver something we often take for granted.
It also makes you think about the impact of your choices. Supporting renewable energy, reducing your energy use, and staying informed about the grid’s future are small ways you can play a part in this evolving story.
So next time your phone hits 100 percent or your heater kicks on in the middle of the night, remember the long journey that energy made just to get to you. It’s not magic. It’s engineering, cooperation, and a lot of moving parts, all working together to power your world!
Now that you understand the incredible system behind your electricity, why not take the next step in choosing where it comes from? With Renaissance Power & Gas, you can support a cleaner, more reliable energy future. Our fixed-rate energy plans help you avoid market volatility and give you peace of mind, all while supporting renewable energy sources. Switch to Renaissance Power & Gas now and take control of your power, because how your energy is made, and who you get it from, truly matters!



0 Comments